Describe Some of the Uses and Drawbacks of Raman Spectroscopy
A typical analysis requires only a few seconds. Fitting a powerful microscope to a Raman spectrometer enables.
Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy 1.
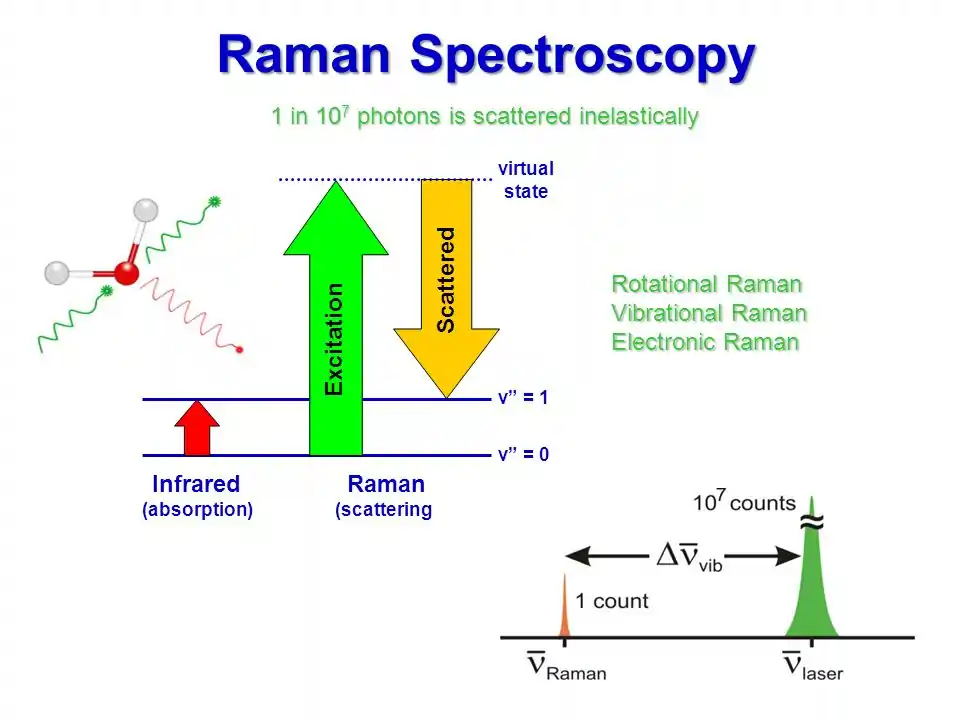
. However in Raman spectroscopy UV VIS or NIR light is used as radiation source which has a much higher energy than those energy differences and absorption of photons is impossible. Raman Spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy has become an incredibly useful analytical technique for the identification of organic inorganic and biological samples. Welcome to the exciting world of Raman spectroscopy.
Since its discovery in the 1920s physicists and chemists have used Raman. The only exception is pure metals which just reflect light. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which.
Two studies are highlighted to demonstrate basic science and. Altangerel et al. It uses light Scientists and engineers can apply the tricks they already know about manipulating light to Raman spectroscopy.
Raman spectroscopy is used to understand more about the make-up of materials. First there is insufficient evidence that Raman spectroscopy can be used to measure changes in the. Raman spectroscopy uses inelastic scattering of photons off covalently bound molecules to identify functional groups crystallinity and stresses and strains.
One of sciences easiest to use most powerful and most versatile analytical techniques. Spectroscopy also finds uses in astronomy to obtain information about the composition density temperature and other principal physical processes of a certain astronomical object. Applications the Future of Raman Spectroscopy.
Thus Raman spectroscopy is suitable for your microscopic examination of cells and proteins. Raman spectroscopy is quick. Raman spectroscopy is an analytical method by which chemical data are obtained through the inelastic scattering of light.
Raman Spectroscopy is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique which provides detailed information about chemical structure phase and polymorphy crystallinity and molecular interactions. Named after Indian physicist C. The laser light is used because it is a very intense beam of nearly monochromatic light that can interact with sample molecules.
Due to the low Raman intensities the detector sensitivity is paramount 2. Material characterization Pharmaceutical analysis. Raman spectra analysis requires extremely small volume 1 µm in diameter sample collection for species identification.
Raman Spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique which is used to analyze vibrational rotational and other low-frequency modes in a system. It is a widely used tool in the spectroscopy community for both quantitative and qualitative molecular analysis with applications ranging from high-end university research to airport. As the name suggests this phenomenon is named after Sir C.
It is a light scattering technique whereby a molecule scatters incident. Spectroscopy is used as a tool for studying the structures of atoms and molecules. Ramans spectroscopy is commonly used in the branch of chemistry to provide a fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
Raman spectra can generally be measured from solids liquids and gases including thin films and powders. Raman is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is an emerging analytical approach that probes the molecular signature of endogenous cellular biomolecules under biocompatible conditions with high spatial resolution.
Raman spectroscopy has been used to support formulation development with applications in aggregation particulates and real-time release of formulation buffers 8789. Raman spectroscopy measures the scattering of light by matter. Applications of Raman spectroscopy in prostate cancer include biopsy analysis assessment of surgical margins and monitoring of treatment efficacy.
A sample is illuminated using a single colour of light and the way the light interacts with the sample tells us. Fluorescence caused by the laser is a major concern with some samples. Overview A vibrational spectroscopy - IR and Raman are the most common vibrational spectroscopies for assessing molecular motion and fingerprinting species - Based on inelastic scattering of a monochromatic excitation source - Routine energy range.
Laser can destroy sections of the sample if the power setting is too high 4. Instead the incident light will excite the system to a high-energy state. However metallurgists use Raman spectroscopy because carbides nitrides and oxides do Raman scatter.
Raman spectroscopy applications include reaction monitoring and the verification and identification of substances including illegal and hazardous materials. It is based upon the interaction of light with the chemical bonds within a material. When matter absorbs light the internal energy of the matter is changed in some way.
Raman spectroscopy ˈ r ɑː m ən. Raman spectroscopy can be used to measure the chemical composition of a sample which can in turn be used to extract biological information. Many materials have characteristic Raman.
Raman spectroscopy is a much more expensive technique to use than IR since high powered lasers and amplification sources are needed to get sensitive. However we believe there are some problems that need to be considered. A major advantage of IR over Raman is the cost.
200 - 4000 cm1 Complementary selection rules to IR spectroscopy. The technique is insensitive to aqueous absorption bands. Other disadvantages of Raman spectroscopy include equipment cost and the sensitivity of the technique.
The light source used in Raman spectroscopy is a laser. Measurements through packaging make it a very safe technique for authorities such as the police first-responders and customs but also for warehouse personnel working as incoming goods inspectors. The large number of wavelengths emitted by these systems makes it possible to investigate their structures in detail including the electron configurations of ground and various excited states.
Instrumentation is more expensive than typical mid-range IR 3. 18th December 2019. Raman spectrophotometers can be quite costly depending on their applications and the technique generally cannot compete with chromatography for analytical sensitivity in quantitative analyses 11.
1 suggest that Raman spectroscopy can be used to detect the early abiotic stress response in plants through the measurement of anthocyanins and carotenoids in plant tissues. Spectroscopy also provides a precise analytical method for finding the constituents in material having.

Raman Spectroscopy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Raman Spectroscopy Applications Anton Paar Wiki


Comments
Post a Comment